In many countries, it’s quite common, and sometimes mandatory, to microchip pets.
The Department of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ho Chi Minh City is proposing that pet owners register their dogs and cats with the local People’s Committee and encourage households to microchip their pets for information management.
Microchipping pets has become a widespread practice in numerous nations, primarily for the purpose of identification and tracking. This process involves implanting a tiny electronic chip under the skin of the animal, usually in the shoulder area. The chip contains a unique identification number that can be read by a scanner. This number is linked to a database containing details about the pet and its owner, facilitating easy identification and reunion in case the pet gets lost.
The initiative proposed by the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development in Ho Chi Minh City reflects a growing trend in pet management policies. By requiring pet owners to register their animals with the local authorities, the aim is to enhance accountability and ensure better control over the pet population. Additionally, the encouragement of microchipping serves to bolster these efforts by providing a reliable method of tracking and identifying pets.
Implementing such measures can have several benefits. Firstly, it can aid in the swift return of lost pets to their owners, reducing the number of stray animals on the streets. Secondly, it enables authorities to monitor pet populations more effectively, which can be crucial for disease control and prevention. Moreover, microchipping can discourage pet theft and illegal breeding practices, as it makes it harder for unscrupulous individuals to sell or pass off stolen pets as their own.
However, while the intentions behind these proposals are commendable, there are practical considerations and potential challenges to address. One such concern is the cost associated with microchipping, which may pose a financial burden for some pet owners, especially in regions where economic constraints are prevalent. Additionally, ensuring widespread compliance with registration and microchipping requirements may require extensive outreach and education efforts to raise awareness among pet owners about the benefits and importance of these practices.
Overall, the initiative to register and microchip pets represents a proactive approach towards responsible pet ownership and population management. By leveraging technology to enhance traceability and accountability within the pet community, authorities can take significant strides towards creating safer and more humane environments for both pets and humans alike.
Microchip for dogs from 8 weeks old
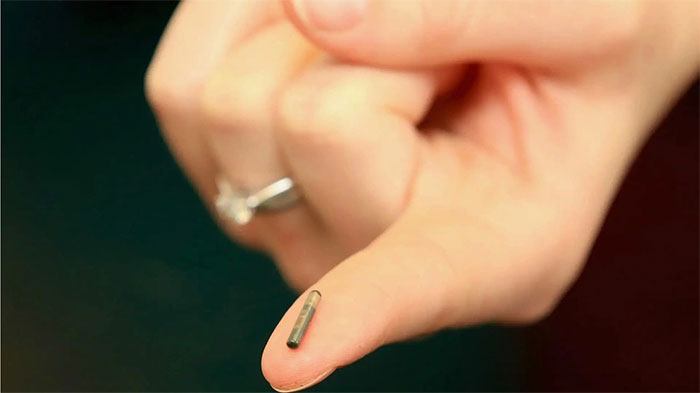
Currently, the most common type of chip used for pets by various countries is the microchip, a tiny electronic chip about the size of a grain of rice, utilizing radio frequency identification (RFID) technology.
An RFID device consists of two components: a reader and a transmitter that emits an identification code. Based on this code, veterinary agencies and governing bodies can gather a wealth of related information such as the owner’s address, phone number, and email, as well as the pet’s name, breed, and vaccination status.
In the United Kingdom, regulations effective since 2016 mandate that pet dogs over 8 weeks old must be microchipped. It is anticipated that from June 2024, the country will propose additional requirements for microchipping cats over 20 weeks old. Violations of these regulations may incur fines.
Within the European Union (EU), most countries enforce microchipping for dogs, while requirements for cats and other pets vary. Some nations also stipulate specific regulations regarding the sale and trade of pets to safeguard both pet owners and animal rights.
From a broader perspective, the introduction of microchipping regulations for pets underscores a growing recognition of the importance of responsible pet ownership and animal welfare. By implementing these measures, authorities aim to enhance traceability, reduce pet theft, and ensure effective disease control within pet populations.
Furthermore, microchipping not only aids in reuniting lost pets with their owners but also plays a crucial role in curbing the proliferation of stray animals, thereby promoting safer and healthier communities for both humans and animals.
While the enforcement of microchipping regulations may encounter challenges such as compliance issues and financial constraints for pet owners, the long-term benefits in terms of improved pet management and welfare far outweigh these challenges. It is imperative for authorities to accompany such regulations with comprehensive education and support initiatives to ensure widespread understanding and adherence among pet owners.
In conclusion, microchipping represents a valuable tool in modern pet management, offering numerous advantages in terms of identification, traceability, and overall animal welfare. By embracing technological advancements and fostering a culture of responsible pet ownership, societies can create safer and more compassionate environments for pets and humans alike.
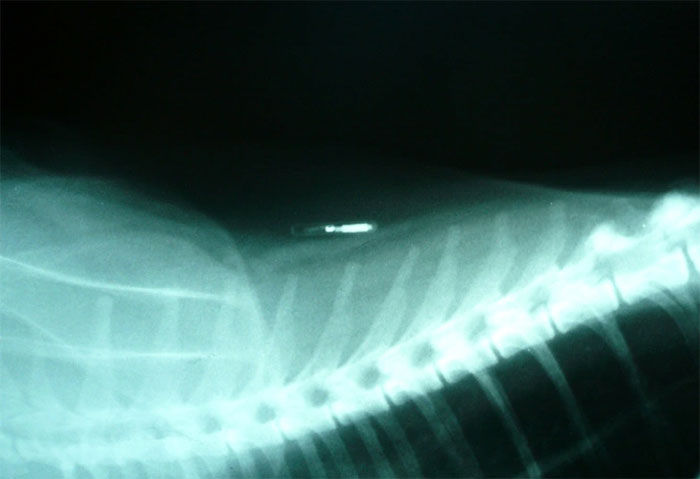
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has issued technical specifications for standardized pet chips, which are widely accepted by most countries. ISO-approved chips carry a 15-digit identification number, while non-ISO chips have 9 or 10 digits.
According to HowStuffWorks, implanting a chip into a pet is a quick and minimally invasive procedure, often performed by veterinarians using a syringe between the dog’s shoulder blades. Typically, the chip remains passively under the skin in the dog’s body. Only when scanned by a reader do they transmit identification information to the device.
The standardization of pet microchips by ISO ensures consistency and interoperability across borders, facilitating seamless identification and tracking of pets globally. By adhering to these standardized specifications, countries can streamline their pet registration and management processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in pet identification.
From a practical standpoint, the insertion of microchips in pets serves as a reliable safeguard against loss or theft, providing pet owners with peace of mind knowing that their beloved companions can be easily traced and reunited if separated. Additionally, microchipping contributes to the responsible stewardship of pet populations, enabling authorities to monitor and regulate pet ownership effectively.
Moreover, the evolution of microchip technology continues to drive advancements in pet care and welfare. With innovations such as GPS-enabled chips and remote monitoring capabilities, pet owners can now track their pets’ movements in real-time and receive instant alerts in case of emergencies, further strengthening the bond between humans and their furry companions.
While the widespread adoption of microchipping represents a positive step towards enhancing pet management and welfare, it is essential to address concerns regarding data privacy and security. As pet microchip databases contain sensitive information about both pets and their owners, robust measures must be implemented to safeguard against unauthorized access and misuse of this data.
In conclusion, the standardization and adoption of microchipping technology for pets reflect society’s commitment to promoting responsible pet ownership and ensuring the well-being of animals. By leveraging technological innovations and international standards, we can create safer, more connected communities where pets can thrive alongside their human companions.
Indirectly reduces dog and cat bites
Research conducted by the University of Florida in the United States indicates that one out of every three pets will go missing at some point. However, data retrieved from microchips shows a higher likelihood of lost pets being reunited with their owners. For instance, surveys conducted at animal shelters in the United States, Italy, and Israel revealed that up to 74% of microchipped pets were successfully reunited with their owners when lost.
Regarding cats, a study published in the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association (JAVMA) found that cats with microchips are over 21 times more likely to be reunited with their owners compared to those without chips.
These findings underscore the importance of microchipping as a valuable tool in pet identification and reunification efforts. By providing a reliable means of linking lost pets to their owners, microchipping significantly enhances the chances of successful reunions, thereby reducing the emotional distress and financial burden associated with lost pets.
Moreover, the benefits of microchipping extend beyond individual pet owners to society as a whole. By reducing the number of stray animals and minimizing the burden on animal shelters, microchipping contributes to the overall welfare and safety of communities.
While microchipping offers clear advantages in pet identification and retrieval, it is essential for pet owners to ensure that their contact information registered with the microchip database is accurate and up-to-date. Regularly updating contact details can expedite the process of reuniting lost pets with their owners, maximizing the effectiveness of microchipping efforts.
In conclusion, the evidence from research studies highlights the significant role of microchipping in promoting responsible pet ownership and enhancing pet welfare. By embracing microchipping technology and implementing effective pet identification strategies, we can create a safer and more secure environment for our beloved animal companions.

Research published in the journal of the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) reveals that microchipping assists veterinary clinics and regulatory agencies in obtaining data on pets, particularly information regarding vaccinations against various diseases. Additionally, the increased likelihood of finding lost pets translates to a decrease in the number of stray dogs and cats.
In the United States, the cost of microchipping for dogs and cats at veterinary clinics typically ranges from $25 to $60. Some animal welfare centers may offer microchipping services for as low as $5.
Microchipping not only aids in the identification and management of pets but also plays a crucial role in promoting public health by ensuring that animals are up-to-date on their vaccinations. By facilitating the tracking of vaccination records, microchips help prevent the spread of infectious diseases among both pets and humans, contributing to overall community well-being.
Furthermore, the economic implications of microchipping extend beyond individual pet owners to society as a whole. By reducing the number of stray animals, microchipping minimizes public health risks, alleviates the strain on animal control agencies, and lowers the costs associated with sheltering and caring for stray animals.
From a practical standpoint, the affordability and accessibility of microchipping services are essential considerations in promoting widespread adoption. By offering low-cost or subsidized microchipping options, veterinary clinics and animal welfare organizations can encourage more pet owners to avail themselves of this valuable service, thereby enhancing pet identification and reunification efforts.
While the initial investment in microchipping may seem relatively small compared to the potential benefits, it is crucial to recognize the long-term value of this preventive measure in safeguarding the health and well-being of both pets and the community at large.
In conclusion, the research underscores the multifaceted benefits of microchipping in promoting responsible pet ownership, protecting public health, and mitigating the challenges associated with stray animals. By prioritizing the widespread adoption of microchipping and ensuring affordability and accessibility, we can create safer, healthier communities for both humans and animals alike.
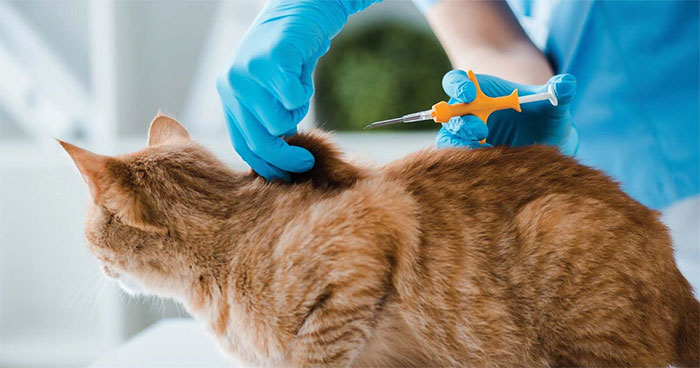
The American Veterinary Medical Association states that the majority of cases involving microchipped dogs and cats do not impact their health. In rare instances, some pets may experience minor reactions such as mild swelling, redness, or, extremely rarely, infection at the injection site.
Although rare, there have been cases where microchips may not function properly. This could be due to manufacturing defects or damage post-implantation. Pet owners are advised by experts to conduct regular checks when visiting veterinary clinics to ensure that the microchip is functioning properly.
While the likelihood of adverse effects from microchipping is low, it is essential for pet owners to be aware of potential risks and to monitor their pets for any signs of discomfort or complications following the procedure. By staying informed and proactive, pet owners can help ensure the safety and well-being of their beloved companions. Regular veterinary check-ups and communication with healthcare professionals are crucial in addressing any concerns related to microchipping and maintaining the overall health of pets.